Carpal tunnel syndrome is
one of the most common hand diseases that causes pain, numbness or tingling in
the hand. This problem occurs when the median nerve of the wrist or carpal
tunnel is compressed. Carpal tunnel syndrome in the early stages is easily
cured by performing simple treatment strategies, but if it progresses, it needs
surgery for treatment. In the rest of this section, we will introduce
carpal tunnel syndrome and provide you with information about its treatment
methods.
What is
carpal tunnel?
The
median nerve is one of the most important nerves of the hand, which starts from
the neck and reaches the wrist after passing through the arm and
forearm. This nerve passes through the carpal tunnel in the wrist area and
finally by passing through the palm, it provides sensation to the fingers and
also controls the muscles around the fingers. In addition to the median
nerve, tendons also pass through the carpal tunnel, which are called flexor
tendons. Flexor tendons are responsible for bending the fingers.
In
fact, it can be said that the carpal tunnel is responsible for protecting the
flexor tendons and the median nerve. This tunnel is made up of a very
tight connective tissue. Therefore, it has a very hard space and cannot be
stretched and increased in volume. Therefore, the narrowing of the tunnel
causes pressure on the median nerve and causes pain, weakness, numbness or
tingling in the hand.
Causes
of carpal tunnel syndrome
According
to research, people who do a lot of work are more prone to carpal tunnel
syndrome. In addition, this disease is more common in women and often
affects the elderly. Carpal tunnel syndrome has several causes, including:
Excessive
use of hands: People who work with their wrists for long periods of time
are more prone to carpal tunnel syndrome. Repetitive hand movements put
pressure on the nerves and cause swelling and pain.
Heredity: Heredity
can be considered one of the most important causes of carpal tunnel
syndrome. Research has shown that some people have a carpal tunnel that is
smaller than normal from the beginning, which reduces the space of the median
nerve and causes carpal tunnel syndrome.
Pregnancy: Hormonal
changes are one of the things that mothers face during pregnancy. These
changes cause the swelling of the carpal tunnel and eventually reduce the space
of the median nerve.
Other
diseases: diseases such as hypothyroidism, rheumatism and diabetes
are among the diseases that may cause carpal tunnel syndrome.
Symptoms
of carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal
tunnel syndrome has signs and symptoms that include:
·
A feeling of pain,
numbness or tingling in the fingers that starts from the thumb and index finger
and finally reaches the index and ring finger.
·
Pain or tingling
sensation that starts in the forearm and slowly moves towards the shoulder.
·
A person with carpal
tunnel syndrome feels weak in the tips of his fingers to the point where he has
trouble closing the buttons of his clothes.
·
A feeling of weakness and
laxity in the hand so that the person is unable to hold objects and causes them
to fall.
The
symptoms mentioned in the beginning are not permanent and appear
occasionally. As the disease progresses, the condition worsens and
symptoms become more pronounced or occur more frequently. The thing about
carpal tunnel syndrome is that the symptoms of the disease show themselves more
at night. Especially people who have a habit of bending their wrists while
sleeping face severe pain that sometimes wakes them up.

Treatment
methods
When
the patient encounters the above symptoms, he goes to the doctor to relieve his
pain. The doctor performs various examinations and tests on the patient to
diagnose the type of disease. Electrophysiology tests, nerve conduction
(NCV), electromyogram (EMG), ultrasound, X-ray imaging, and MRI are some of the
things that a doctor uses to diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome.
After
diagnosing the disease and examining the tests, the doctor evaluates the
patient's condition and considers the necessary treatment for him according to
the progress of the disease. Carpal tunnel syndrome develops gradually and
if it is in the early stages, it can be treated with simple non-surgical
methods. In fact, the doctor tries to reduce or completely stop the
progression of the disease by using a brace, doing certain exercises and
sports, changing the patient's activities, etc. If the disease is in
advanced stages, the doctor has no choice but to operate.
Carpal
tunnel syndrome surgery
If the
non-surgical treatments have no effect and the patient still faces symptoms
such as pain and numbness, the doctor suggests surgery. The purpose of
surgery is to remove pressure from the median nerve, which is called
"carpal tunnel release". Carpal tunnel release is done in two
ways:
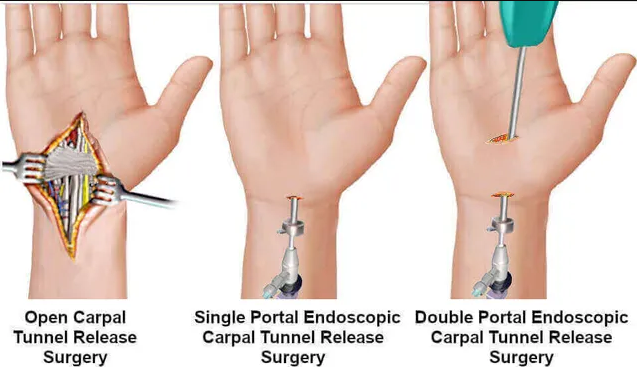
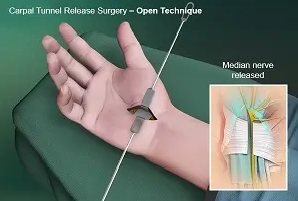
First
method: In this method, the surgeon makes a small incision on the palm so that
he can access the inner parts of the hand. In this method, the two parts
of the transverse carpal ligament are separated to increase the volume of the
tunnel and remove the pressure from the nerve.
Endoscopic
method: In this method, the surgeon uses a small device called an endoscope to
view the internal components of the hand and release the carpal
tunnel. The endoscope device has a camera and a light source that enters
the body through a very small incision on the skin.
Postoperative
care of carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal
tunnel syndrome surgery, like other surgeries, requires care, which includes:
·
Immediately after the
operation, the surgeon asks the patient to hold his hand above the heart and
move his fingers. In fact, this prevents the fingers from getting stiff.
·
Pain in the palm area is
one of the complications after carpal tunnel syndrome surgery, which may last
for several weeks after the operation.
·
Weakness and inability to
pick up objects usually lasts 2 to 3 months after the operation, but in some
cases it lasts between 6 and 12 months.
·
The patient must use a
brace or splint for the wrist for a few weeks after the operation.
·
It is not a problem to
carry out light activities and tasks such as lifting objects, driving, personal
activities, etc. a few days after the operation.
·
Arthritis, tendon
inflammation, weakness and pain are normal up to 2 months after the operation
and gradually improve. If this time is prolonged, the doctor will suggest
physiotherapy for faster treatment.